It’s not enough to make a plantation and creating a rearing house, we must protect them from pests and disease. If we don’t prevent mulberry plants and silkworm from pests & disease, they can destroy our whole sericulture plan. This post helps you to identify the problems and solve them with correct solutions.
Mulberry – Pests and Disease
Pests in mulberry
- Pink mealybug,
- Papaya mealybug,
- Leaf webber,
- Thrips,
- Termite,
- Cutworm,
- Hairy caterpillar,
- Grasshopper,
- Jassid (leaf hopper),
- Scale insect,
- Mulberry Leaf Roller.
DDVP(Dichlorvos) should be sprayed 20 days after pruning and safety period is 10 days
DDVP usage
1.Pink mealybug
Maconellicoccus hirsutus is commonly known as pink mealybug or grape, hibiscus mealybug sucks the cell sap from leaves and buds, leaves became dark green, thick and wrinkle. Affected portions will brittle and leaves will be pale yellow. These insects will make the short internodal distance, they attack the leaves throughout the year although severe in summer. They reduce nutritive value and affect the yield of leaves by 4,500 kg per hectare.
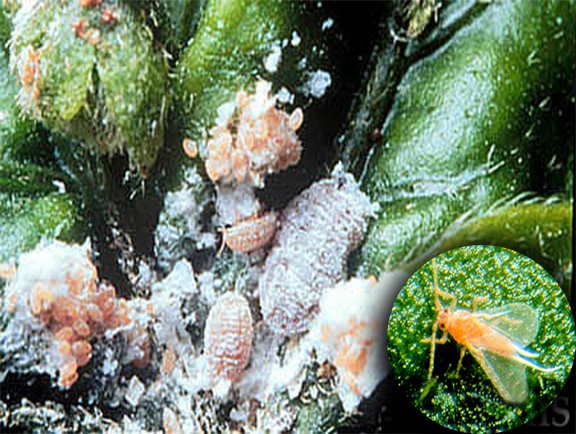

Management- We should cut the affected shoots and destroy it by burning it in the fire, burning will help to reduce the chance of recurrence of the insect. We can release predators like ladybirds or we can spray FORS(Fish Oil Rosin Soap) these methods are organic. We can also use chemical pesticides like DDVP(Dichlorvos)in 76 % in the mixture of 2.6 ml/lit after pruning.
2.Papaya mealybug
Paracoccus marginatus commonly called the papaya mealybug, these bugs attack on fruits and vegetable plants. These insects affect top part and leaf bud initially and then it spreads all over the mulberry plants, they spread all over the plant in some intervals.
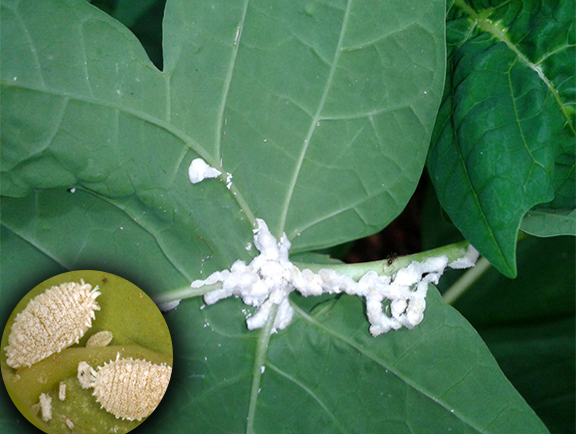

Management – We can’t control them by any pesticides, we can control them with the help of sprinkler irrigation by irrigating the plants in continuous intervals these papaya mealybug flies has very less chance to spread and we can also release exotic parasitoid like Acerophagus papayae
Acerophagus papayae @1 vial per acre
Acerophagus papayae parasitoids RELEASE rate
3.Leaf webber
Crocidolomia Binotalist commonly called a leaf Webber and they are a moth, they damage the plant and reduce the leaf yield. They cause damage by folding leaves and webbing it, these larvae web leaves and fed from the soft parts and make them look like a skeleton, they affect the quality of leaves and yield is severely affected.
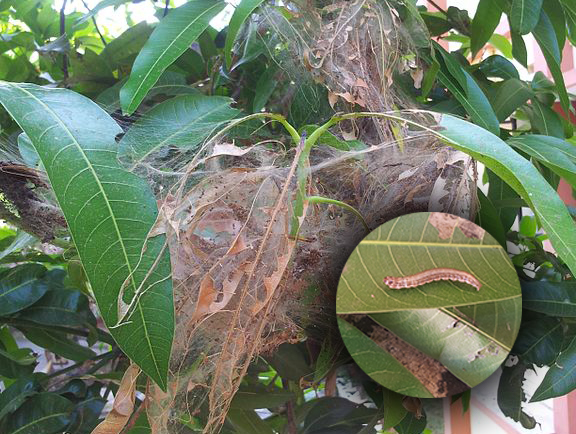

Management– We can release of the pupal parasitoid (Tetrastichus howardi ), spraying DDVP(Dichlorvos) in 1 ml/l will help us to keep leaf Webber away, the release of egg parasitoid (trichogramma chilonis ) and even mechanical clipping and burning of the affected shoots also control these insects.
4.Thrips
Thrips (order of thysanoptera ) they spread mainly during the summer, they tear the leaf tissues and suck the sap, we can find affected leaves in an early stage by the change in colour and we can see the leaves has early maturity these leaves will become unfit for silkworms
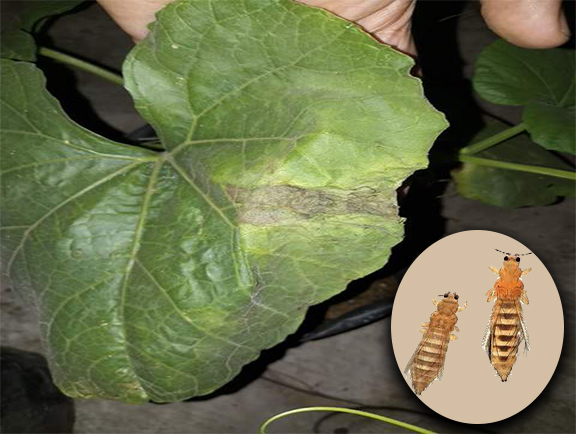

Management- We can use sprinkler irrigation to control insect population and eggs if these insects continue to spread we can try chemical method by spraying 0.1% Rogor @3ml/l
After releasing parasitoids we should not spray any chemical fertilizers or pesticides or insecticides
parasitoids MANAGEMENT
5.Termite
They are eusocial insects (like ant, bees and vespides) they build their nests with mud attached to the plant and eat plant from the stem.
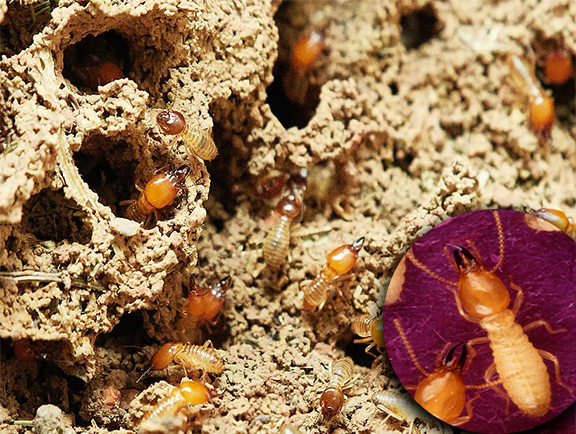

Management – We can use pesticides like Lindane 20% or Chlorpyrifos 20% or imidaclopride 30.5% , we can also eliminate them by removing the queen termite .
6.Cutworm
They are month larvae, they hide under the soil during the day and feed plants on the night. The caterpillar feeds on young mulberry leaves, they spread on monsoon period
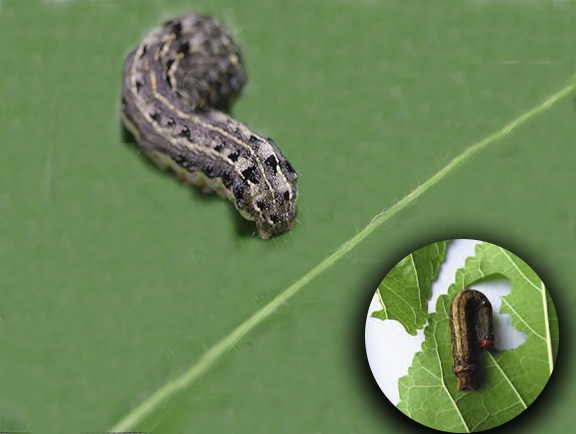

Management- As usual we can spray DDVP(Dichlorvos) @ 2ml/l we should spray after evening .
Egg parasitoids (Trichogramma chilonis) should be release @ 1 Tricho card/week for 4 weeks
Egg parasitoids release rate
7.Hairy caterpillar
These hairy caterpillars have many varieties like Metanastria hyrtaca (hairy caterpillar), Amsacta albistriga (red hairy caterpillar), Spilosoma obliqua (Bihar hairy caterpillar or jute hairy caterpillar ), Psalis pennatula (yellow hairy caterpillar) these caterpillars are larvae of the moth family. These hairy caterpillars attack mulberry plants on monsoon, young ones attack leaves from the downside gregariously we can’t find the caterpillar from the distance

Management-0.15% DDVP can be sprayed @2ml/l of water and we can release egg parasitoids (Trichogramma chilonis ) and we can collect them manually and destroy them.
Neorthecris acuticeps nilgirensis are wingless grasshopper species lives in Asia-Tropical, Indian Subcontinent, India, Nilgiri Hills, Hill Grove
Neorthecris acuticeps nilgirensi
8.Grasshopper(wingless)
Grasshopper (cealifera and Neorthecris acuticeps nilgirensis) attacks on monsoon and post-monsoon , these insects mostly feeds buds, soft leaves and green bark.
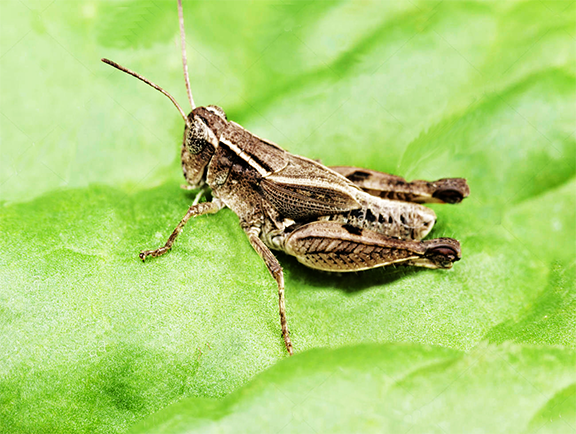

Management – We can spray DDVP at 1 ml/l water on mulberry plants to kill adults and to kill eggs we should plough the land then the egg will be exposed to the sun and predators.
These information is not for locust attack to read more about locust click here
9.Jassid (leaf hopper)
Amrasca biguttula are from the family of cicadellidae commonly leaf hopper (they are also called as a cotton jassid ) they attack mulberry plants spring and autumn season ,these leaf hoppers are very active insects and they jump over side ways .They eats sap and we can find yellowish in the leaf margin and leaf became cup shape in the final stage .
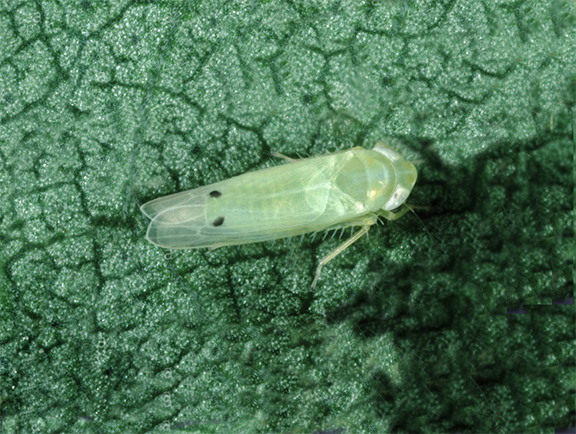

Management- we can spray rogor 0.1% and we can keep sticky traps or light traps .
10. Scale roller
These insects are from the order of hemiptera and suborder of sternorrhyncha , these are very small insects spreads severely during summer. we can find them sticking under the leaves and stem, like as many insects they feed on sap and make the mulberry plant to die
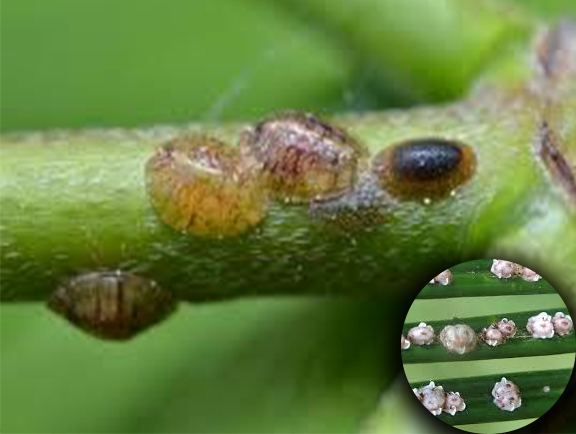

Management – We can manually peel them from the stem and leaves and destroy them or we can spray rogor 0.05% or 0.15% DDVP both in 2 ml /l in water.
11.Mulberry leaf roller
Diaphania pulverulentalis commonly called as a Mulberry leaf roller in the family of Crambidae, they start their attack during the summer and monsoon season. They roll leaves with the help of their webs and feed on the inside

Management –Spray DDVP 0.076% @ the mixture of 1 ml/l in water and we can also spray neem pesticides @5ml\l in water after seven days and we can release egg parasitoid or we can manually collect the affected leaves and burn them.
Diseases in Mulberry plant
- Leaf spot,
- Leaf rust,
- Powdery mildew,
- Fungal leaf blight,
- Bacterial leaf blight,
- Root-knot nematode,
- Root rot.
1.Leaf Spot
In mulberry leaf we can find the round spot which is caused by Cercospora capsici (fungal plant pathogen), these fungal attacks occur on the rainy and winter season especially 40 days after pruning. Leaf spot is an air-born disease caused by water droplets and winds current, the disease develops according to the temperature and high humidity.
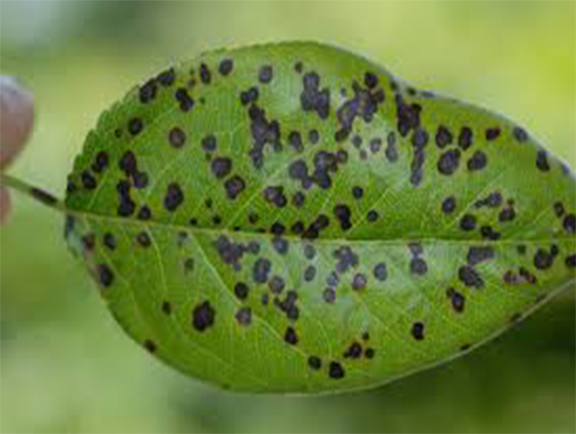

Management – we can avoid them by spraying Carbendazim 50 wp on leaves @ 500-625 g/ha.
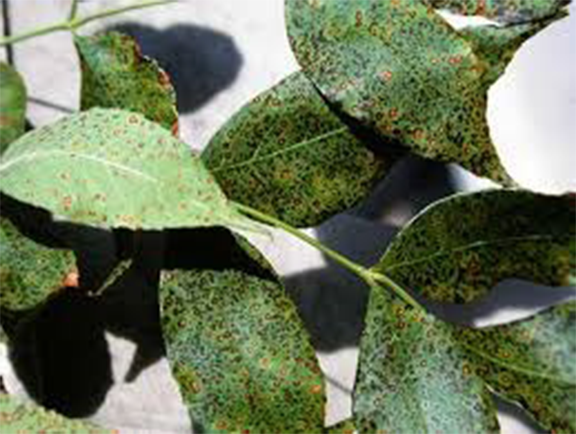
2.Leaf rust
Leaf rust is a fungal disease caused by Cerotellium fici , this disease spread during winter and rainy season, mature leaves are easily attacked by the disease. In the beginning stage, we can see circular brown spots on the leaf and later leaf became yellowish and wither off . Both leaf rust and leaf spot are similar they are air-born disease and spreads in the condition of high humidity and temperature.
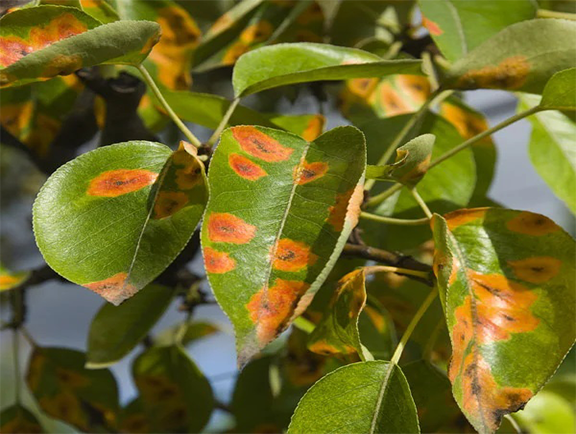

Management – We can use chemical spray Chlorothalonil 75% on leaves, leaves must be harvested on time and spacing for the plantation should be done in recommended spacing (given in mulberry cultivation article)
3.Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease caused by Phyllactinia, we can see white powdery patches on the leaf in the initial stage, and then the entire leaf is covered, later white color turns to black and brown, next leaves will turn to yellow and fall. As usual like all fungal disease outbreak in the temperature and high humidity.
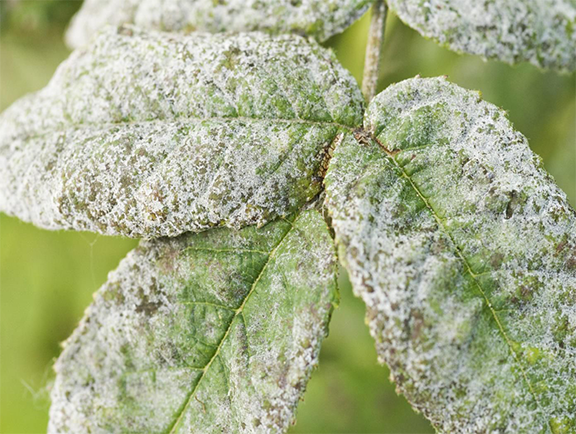

Management- Releasing yellow ladybird will help in reducing the fungal, we can spray Carbendazim and Dinocap 30%ec or we can spray Sulfex 80wp and also proper spacing should be followed.
4.Fungal leaf blight
Fungal leaf blight start to affect the leaf tip and edges and afflicted area looks like brown or black colour ,then it continues to affect the leaf and falls down.This is a air-born disease spreads through water droplets and winds current ,it spreads on high humidity and temperature .

Management – Spray Mancozeb 75% wp , proper spacing for plants and cut and destroy the leaves manually.
5.Bacterial leaf blight
This disease specifically affects the mulberry plant this disease spreads on winter and rainy season , this disease is both soil and air born and they mostly spreads on high humidity and hih temperature .We can find black and brown water soaked patches which starts to rotting and curling leaves .
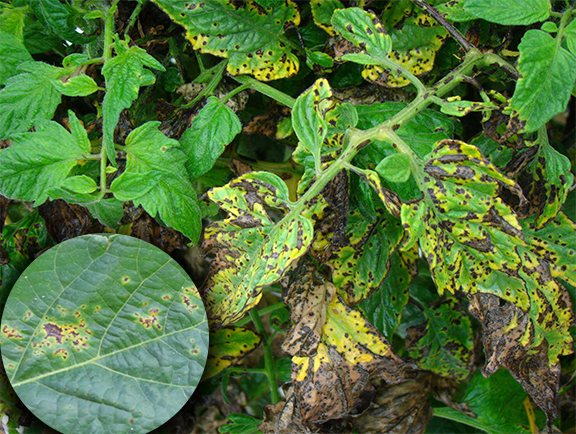

Management – Spray 0.2% mancozeb 75%wb and 0.2 % streptomycin ,we should maintain plant spacing and we can cut the leaves manually and destroy it.
6.Root-knot nematode
This is a plant-parasitic nematode these are found in sandy soils which we can see in irrigated areas, we can see low moisture content in leaves and later yellow in margins of leaves, we can see roots are affected by knots on them. In contaminated soil this disease spreads and also in canal irrigation because it creates sandy soils, it spreads in high temperature and medium soil moisture.

Management – Deep plouging during the summer ,applying neem cake at 1000 kg/ha or we can apply Carbofuran @30kg/ha/year in four doses .
7.Root – rot
These disease rot and decay roots of the mulberry plants caused by rhizoctonia bataticola , hey attack plants during the summer, hen the soil moisture is low . highly affected plants will be easily uprooted and the system gets decayed and plants die, hey spread in contaminated soil, arm implements, and irrigation.
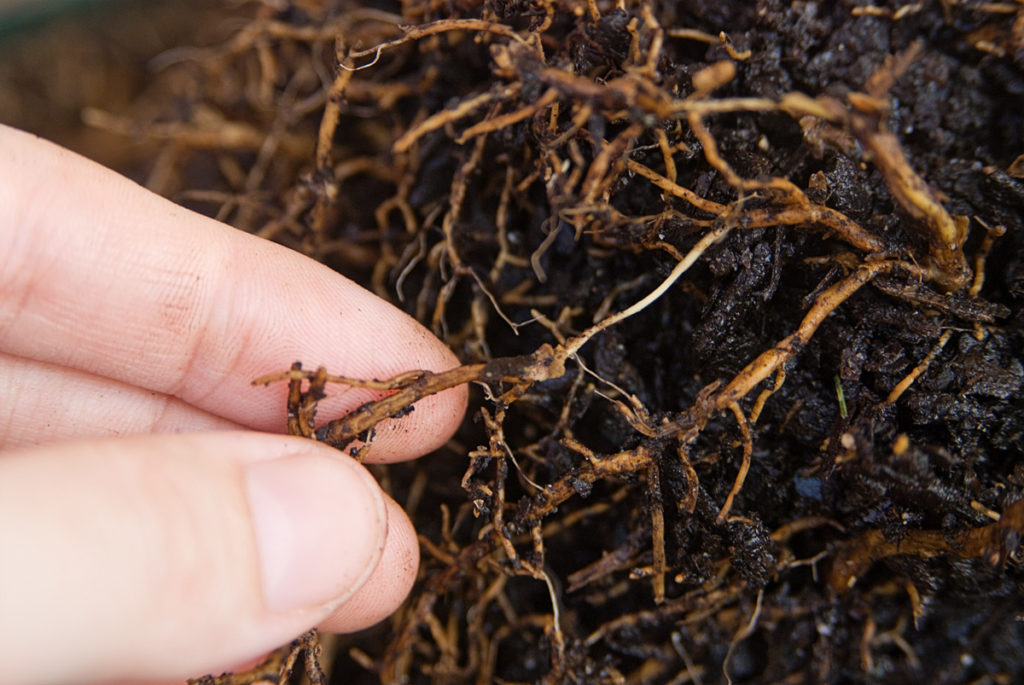

Management – We can apply manure , pull out the affected plants, asin irrigation, e can apply Bacillus substilis @ 25gm/plant or Trichoderma viride @25mg/p and on the surface pour copper oxychloride @2mg /l in water.
You can use any suggested or similar pesticides or herbicides in the country
SUGGESTION
Silkworm -Pests and Diseases
Pests in Silkworms
- Dermestid beetles
- Uzi fly
1.Dermestid beetles
These beetles are family of Coleoptera commonly known as skin beetles, they attack cocoons in the storage. Usually, females lay more or less than 250 eggs in cocoons, if we didn’t notice we will lose all cocoons in our storage. They affect the abdominal region of moths, these beetles will affect our entire sericulture plan.
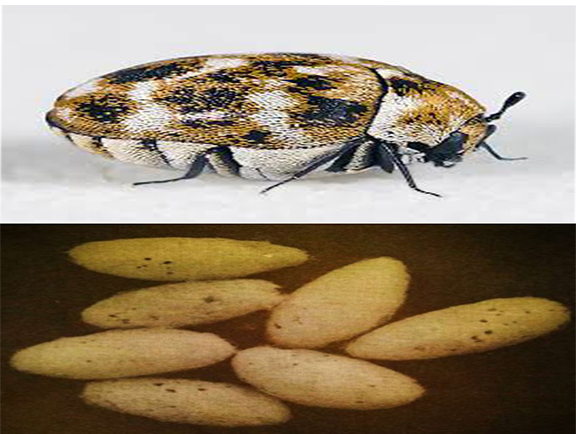

Management- We should clean the rearing house and our cocoon storage room should be cleaned and sterilized regularly if we see any beetles in our storage room or house we should check every cocoon and remove affected cocoons and storing of rejected cocoons and perished eggs for a long time must be avoided. Providing mesh nets on windows, doors, and gaps will keep beetles out of the storage room and rearing house. We can spray 0.028% of Deltamethrin and chlorine on walls and floors once in three months
2.Uzi fly
Exorista sorbillans commonly known as Uzi fly a family of Tachinidae these are serious parasitoid of silkworms, mature fly reuse the yield of the cocoon and reduce the cocoon quality, they also cause the death of silkworm, we can find white oval eggs and a black scar on the skin of larvae in the starting stage and larvae will die before we take them for spinning stage at final stage we can notice pierced cocoon, uzi flies attack all over the year and more in winter
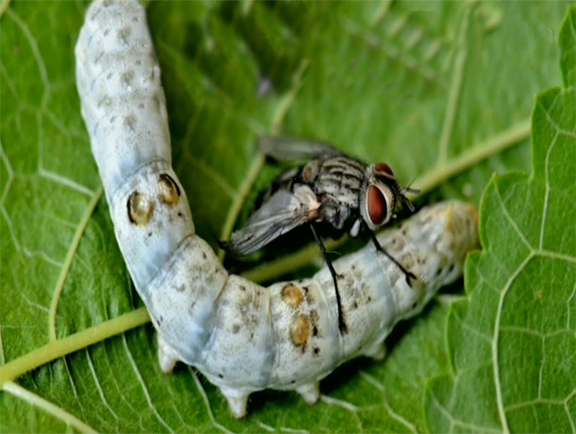

Management – We can provide mesh nets on all doors, windows,and gaps,close all doors and windows.Clean rearing room keeps them hygienic and sanitize them regularly,we can spray 1% of benzoic acid on the larvae to kill eggs of flies.We can release parasitoid Nesolynx thymus inside the rearing house
Diseases of Silkworms
- Fungal disease
- Viral disease
- Protozoan disease
1.Fungal disease
Muscardine is a fungal disease of insects it affects silkworms this disease also called calcino, these fungal disease attack during rainy and winter season, due to low temperature and high humidity they spread. We can see the larvae lose their appetite and it seems inactive, these fungi are common in young age worms and they die. We can see a moist speck on the skin then larvae vomits after the death we can see the larvae were mummified then the body turns chalky white or green colored structure.
Management- We should dry the rearing appliances in the sun, by using the chlorine powder disinfect the rearing, we should avoid low temperature and high humidity in the rearing room and also avoid touching the equipment with wet hands, keep the rearing bed thin and dry, we can apply dithane as the disinfectant on the larvae and pickup indicted larvae before mummified.
2.Viral disease
Grasserie and Flacherie
Grasserie –This disease spreads mostly during the summer and rainy season. Silkworm gets this infection from contaminated leaves and contaminated rearing houses, low humidity, high temperature, and poor mulberry leaf are the source for the infection. We can find the skin of larvae was affected and looks shining, the color of the body became yellow, and inter sentimental swelling will occur.
Flacherie – We can see the larvae becoming soft and flaccid and worms become inactive and vomit, head and thorax of larvae become lighter, due to toxicity sudden death accrue and larvae turn black and we can observe unpleasent smell.
Management – Clean the rearing equipment and rearing house with recommended disinfect like formalin solution or decol or slaked lime solution or chlorine or any recommended solution, we should be sterilized and hygiene our self and rearing house, collect the infected larvae and properly dispose of it, maintain the correct temperature and good humidity, then we should dry the appliances in sun and provide a proper bed spacing and avoid injury to the larvae.
3.Protozoan disease
Pebrine is a protozoan disease it causes irregular hatching of silkworm eggs and make the worms to be inactive and make the skins wrinkle, we can see the small black round appears in the infected worms and makes the larvae to grow slow, undersized and poor appetite and death larvae will be rubbery.
Management – We should disinfect the rearing house and surroundings by recommended disinfectant like chlorine and slaked lime solution and we should produce healthy eggs, maintain strict hygienic condition on rearing, collect and burn the infected eggs, larvae, pupae, and moths and we should maintain seed crops constantly to eliminate the infection.